Flipped Classroom: Everything You Need To Know To Make It A Success!
18th September 2024

The educational landscape is constantly evolving, with technology playing a transformative role in reshaping how students learn. One of the most significant innovations to emerge in recent years is the flipped classroom model. This pedagogical approach flips the traditional instructional method, moving the lecture out of the classroom and bringing hands-on activities into it. In this guide, we’ll delve deep into the flipped classroom: its definition, history, benefits, challenges, implementation, and best practices.
What is the Flipped Classroom?
The flipped classroom is a teaching approach that reverses the typical learning environment. Instead of students listening to a lecture during class and then doing homework afterward, they watch pre-recorded lectures or read materials at home. The classroom time is then used for engaging activities such as discussions, problem-solving, group work, or hands-on projects.
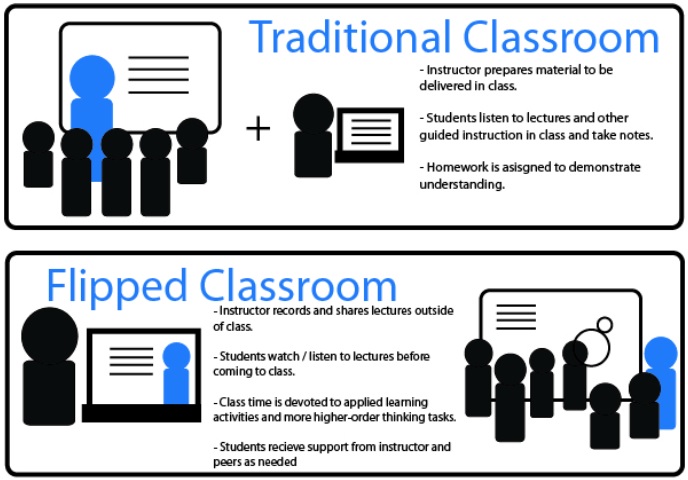
Source: slu.edu
In a traditional classroom, teachers spend most of the class time delivering lectures, and students often complete assignments or projects outside the class. In contrast, the flipped classroom model allows students to first engage with new content at their own pace, typically through online videos, readings, or other multimedia resources. Then, in class, they apply what they've learned under the guidance of their instructor.
Do you follow us on Social Media? If not, then you’re missing out on a lot of informative content. We regularly share upgraded educational content, tips, feedback, and more. Check us out by clicking the profiles here – Facebook / Twitter / LinkedIn / Pinterest / Instagram / YouTube
Key Features of the Flipped Classroom
Here are the few features of a flipped classroom that you should be mindful about:
- Pre-Class Learning
Students are introduced to new material before class through videos, readings, or other digital resources. This pre-class content serves as a replacement for the traditional lecture.
- Active Learning in Class
The in-class time is used for engaging activities, including discussions, problem-solving, debates, case studies, and collaborative work, which allows students to apply what they’ve learned and deepen their understanding.
- Self-Paced Learning
Since students are engaging with the lecture materials on their own time, they can learn at their own pace. This flexibility allows students to pause, rewind, or fast-forward through content, enhancing their understanding.
- Teacher as a Facilitator
The role of the teacher shifts from a “sage on the stage” to a “guide on the side.” Instead of merely delivering content, the teacher becomes a facilitator who helps students apply the material and provides individualized support.
Benefits of the Flipped Classroom
The flipped classroom offers several benefits that can enhance both teaching and learning. This includes:
- Increased Student Engagement
By freeing up class time for interactive activities, the flipped classroom promotes active learning, which has been shown to improve student engagement and retention of information. Students are encouraged to take ownership of their learning.
- Personalized Learning
Since students can engage with the lecture material at their own pace, the flipped classroom allows for more personalized learning experiences. Students who need more time to grasp certain concepts can rewatch videos, while those who grasp the material quickly can move on to more advanced topics.
- Improved Teacher-Student Interaction
Flipping the classroom creates more opportunities for teachers to provide individualized feedback and support. Instead of spending class time lecturing, teachers can work one-on-one with students or in small groups, addressing their specific needs.
- Higher Order Thinking
The flipped classroom model emphasizes higher-order thinking skills such as analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. By using class time for hands-on activities, students have the opportunity to apply what they've learned, collaborate with peers, and tackle complex problems.
- Flexibility for Students
The ability to access lecture material online gives students flexibility in when and where they learn. This can be especially beneficial for students who may have busy schedules or varying learning styles.
Challenges of the Flipped Classroom
Despite its many advantages, the flipped classroom also presents some challenges:
- Access to Technology
The flipped classroom relies heavily on technology, including access to the internet and devices like computers or tablets. Students without reliable access to these resources may struggle to engage with the pre-class content.
- Preparation Time for Teachers
Developing high-quality videos and online materials can be time-consuming for teachers. Additionally, planning and engaging in class activities that effectively reinforce the pre-class material requires careful thought and preparation.
- Student Accountability
The success of the flipped classroom model depends on students taking responsibility for their learning. If students do not watch the videos or engage with the pre-class material, they may be unprepared for in-class activities.
- Classroom Management
Shifting from a traditional lecture format to a more interactive classroom can present classroom management challenges, especially if students are not used to working in groups or participating in hands-on activities.
How to Implement the Flipped Classroom
Implementing a flipped classroom requires thoughtful planning and a shift in both teaching style and mindset. Here are a few things you can do:
1. Create Engaging Pre-Class Content
To ensure students engage with the material before class, it’s essential to create or curate high-quality, engaging content. This might include videos, podcasts, articles, or interactive online modules. Keep the content concise and focused on key concepts.
2. Develop Interactive In-Class Activities
Plan activities that promote active learning and collaboration. These might include group discussions, problem-solving exercises, case studies, or hands-on projects. Make sure the activities require students to apply what they’ve learned from the pre-class material.
3. Monitor Student Progress
To ensure accountability, use quizzes, discussion boards, or other assessments to monitor students' engagement with the pre-class content. Many educators use tools like Google Forms, Kahoot!, or Edpuzzle to create interactive quizzes that help reinforce the material.
4. Provide Continuous Feedback
During in-class activities, circulate the room, offer feedback, and help students who may be struggling with the material. The flipped classroom model creates more opportunities for real-time feedback.
Best Practices for the Flipped Classroom
- Start Small
If you're new to the flipped classroom model, start by flipping just one lesson or unit. Gradually expand the approach as you become more comfortable with the model.
- Be Flexible
The flipped classroom may not work for every lesson or every group of students. Be flexible and willing to adapt the model to fit the needs of your students.
- Encourage Collaboration
Incorporate group work and peer collaboration into your in-class activities. Working together helps students learn from each other and deepen their understanding of the material.
- Gather Feedback
Regularly ask students for feedback on the flipped classroom experience. This can help you identify what’s working well and where there may be room for improvement.
Bottom Line
The flipped classroom represents a dynamic shift in the way we approach education. It emphasizes active learning, personalized instruction, and flexibility, making it a powerful tool for educators looking to engage their students more deeply. As educators who have pursued the International Teaching Diploma Course in Indonesia, you can thoughtfully implement this approach and adapt it to fit the needs of your students. You can create a learning environment that fosters deeper understanding and a lifelong love of learning.
We believe education should be accessible to everyone. That’s why we don’t charge for our blogs. Find the right course that will help you in your career with us, contact us at - 6531631068. You can mail us at act@asiancollegeofteachers.com.
Written By : Sanjana



